Internal organs are the vital components of the human body that play an essential role in maintaining our health and well-being. These organs work together to perform complex functions and processes that are necessary for our survival. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the various internal organs in the human body, their functions, and the role they play in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
The Major Internal Organs and Their Functions
The Brain and Nervous System
The brain is the body’s control center, responsible for regulating bodily functions and cognitive processes. It is composed of over 100 billion nerve cells and is responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting sensory information throughout the body. The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves that connect the brain to the rest of the body. It plays a crucial role in controlling movement, sensation, and cognitive function.
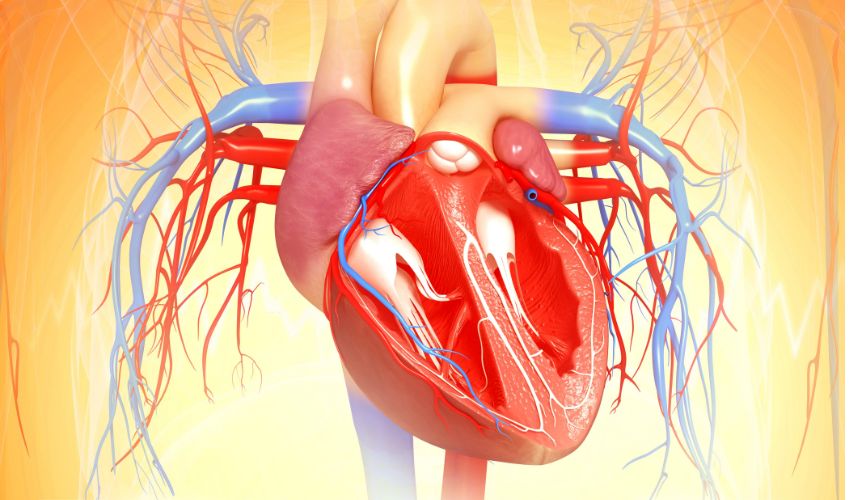
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to internal organs and tissues. It is part of the cardiovascular system, which includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. The heart works continuously, contracting and relaxing to pump blood through the body.
The Lungs and Respiratory System
The lungs are responsible for facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body, allowing for proper respiration. The respiratory system includes the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles. The lungs are composed of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, where the exchange of gases occurs. Oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide is eliminated through exhalation.
The Liver and Digestive System
The liver is the largest internal organ in the body, responsible for aiding in digestion and metabolism. It produces bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats and absorbs nutrients from food. The digestive system includes the liver, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. It is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that the body can absorb and eliminate waste products.
The Kidneys and Urinary System
The kidneys are responsible for removing waste and excess fluids from the blood, helping to regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, which are then eliminated from the body through urine.
The Structure of Internal Organs
Internal organs vary in structure and composition, but all play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s functions. Most internal organs are composed of specialized cells and tissues that work together to perform specific functions. Proper blood flow is essential for the proper functioning of internal organs, as blood delivers oxygen and nutrients and removes waste products. Connective tissue, such as ligaments and tendons, helps to support internal organs and maintain their structure.
Common Diseases and Disorders of Internal Organs
Diseases and disorders of internal organs are common and can lead to serious health problems. Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, with risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Respiratory disorders, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can lead to breathing difficulties and reduced lung function. Digestive disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can lead to malnutrition and dehydration. Kidney disease, such as chronic kidney disease and kidney stones, can lead to kidney failure and other health problems. Neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, can affect the brain and nervous system and lead to cognitive and motor impairments.
Maintaining Healthy Internal Organs: Tips and Strategies
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for keeping internal organs healthy and preventing diseases and disorders. Eating a healthy diet rich in nutrients, vitamins, and minerals is important for providing the body with the energy and nutrients it needs to function properly. Regular exercise can help improve
Bullet Points:
- The human body contains numerous internal organs, each with a specific function and purpose.
- The brain is responsible for controlling bodily functions and cognitive processes.
- The heart pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to internal organs.
- The lungs facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, allowing for proper respiration.
- The liver aids in digestion and metabolism, filtering toxins and waste from the body.
- The kidneys remove waste and excess fluids from the blood, helping to regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
- Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death worldwide.
- Digestive disorders can lead to a range of health problems, including malnutrition and dehydration.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing diseases and disorders of internal organs.
FAQs:
What are the most important internal organs in the human body?
The brain, heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys are among the most important internal organs in the human body.
How do internal organs work together to maintain overall health?
Internal organs work together through complex processes and systems to maintain overall health, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and urinary systems.
What are some common diseases and disorders of internal organs?
Common diseases and disorders of internal organs include cardiovascular disease, respiratory disorders, digestive disorders, kidney disease, and neurological disorders.
What can I do to maintain healthy internal organs?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding risky behaviors, staying hydrated, and getting regular health check-ups can help maintain healthy internal organs.
Can internal organ damage be reversed?
In some cases, internal organ damage can be reversed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. However, in other cases, irreversible damage may occur.
Conclusion:
Internal organs are the cornerstone of the human body, playing a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being. These vital organs work together through complex processes and systems to facilitate the proper functioning of our bodily processes. Understanding the significance of internal organs, their functions, and structure is crucial to maintaining optimal health and preventing diseases and disorders. By taking care of our internal organs through a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, and proper treatment, we can ensure their proper functioning and maintain overall health for years to come. Remember, our internal organs are an integral part of who we are, and it is our responsibility to take care of them.






















