Carotenoids are natural pigments found in plants that give them their characteristic colors ranging from yellow to orange and red. These pigments are not only responsible for the vibrant colors of fruits and vegetables but also offer various health benefits to the human body. Carotenoids play an essential role in the human diet as they cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through dietary sources. In this article, we will explore the health benefits of carotenoids and the foods that are rich in these pigments.
What are Carotenoids?
Carotenoids are natural pigments found in plants that provide numerous health benefits. These pigments are responsible for the bright red, orange, and yellow colors in fruits and vegetables. There are more than 700 different carotenoids found in nature, but only about 50 of them are present in the human diet. The most common carotenoids found in foods are beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin.
Carotenoids act as antioxidants, which means they protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, which is associated with various diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and aging. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals and prevent cell damage.

In addition to their antioxidant properties, carotenoids also have specific health benefits. For example, beta-carotene is converted to vitamin A in the body, which is essential for eye health and immune function. Lutein and zeaxanthin are important for eye health and have been shown to reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Lycopene has been associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Carotenoids are not produced by the human body, so they must be obtained through the diet. Including a variety of carotenoid-rich foods in the diet is important for overall health. Some examples of foods rich in carotenoids include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, broccoli, papaya, mango, and tomatoes.
However, the bioavailability of carotenoids can be affected by various factors such as food processing and cooking methods. Boiling or steaming may decrease carotenoid content in foods, while roasting or grilling may increase their bioavailability. Adding a small amount of healthy fats such as olive oil or avocado can also enhance carotenoid absorption.
While supplements such as beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene are available, it is always recommended to obtain nutrients from whole foods rather than supplements. Consuming excessive amounts of carotenoids from supplements may cause a temporary orange-yellow discoloration of the skin called carotenemia. However, this is not harmful and usually resolves once the intake is reduced. It is generally safe to consume carotenoids from whole foods in recommended amounts.
Bullet Points:
- Carotenoids are natural pigments found in plants.
- They cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Carotenoids play a crucial role in various physiological functions in the human body.
- Beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin, alpha-carotene, and cryptoxanthin are the most common types of carotenoids.
- Carotenoids act as antioxidants and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin are essential for eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Carotenoids may reduce the risk of certain types of cancers, including lung, breast, and prostate cancer.
- Consumption of carotenoids may lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Leafy greens, orange and red fruits and vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and herbs and spices are rich in carotenoids.
- Food processing, fat content, cooking methods, and individual variation affect carotenoid absorption.
- The recommended daily intake of carotenoids varies depending on age, sex, and health status.
FAQs:
What are the benefits of eating foods rich in carotenoids?
Carotenoids act as antioxidants and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. They may reduce the risk of certain types of cancers, lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and promote eye and skin health.
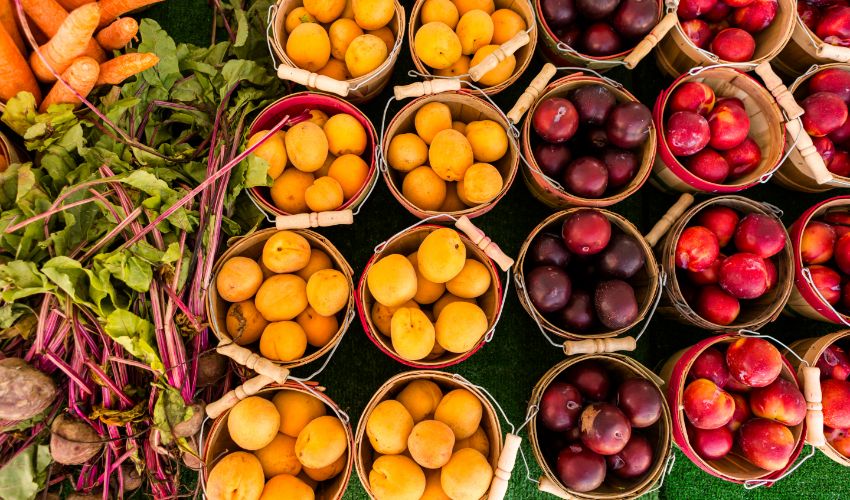

What are the best food sources of carotenoids?
Leafy greens, orange and red fruits and vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and herbs and spices are rich in carotenoids. Some examples include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, broccoli, papaya, mango, and tomatoes.
How do cooking methods affect carotenoid absorption?
Cooking methods such as boiling or steaming may decrease carotenoid content in foods, while roasting or grilling may increase their bioavailability. Adding a small amount of healthy fats such as olive oil or avocado can also enhance carotenoid absorption.
Can supplements be used to increase carotenoid intake?
Yes, supplements such as beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene are available in the form of capsules or tablets. However, it is always recommended to obtain nutrients from whole foods rather than supplements.
Are there any risks associated with consuming too many carotenoids?
Consuming excessive amounts of carotenoids from supplements may cause a temporary orange-yellow discoloration of the skin called carotenemia. However, this is not harmful and usually resolves once the intake is reduced. It is generally safe to consume carotenoids from whole foods in recommended amounts.
Conclusion:
Carotenoids are natural pigments found in plants that provide numerous health benefits. They act as antioxidants and protect cells from damage, promote eye and skin health, and reduce the risk of certain types of cancers and cardiovascular diseases. Including a variety of carotenoid-rich foods in the diet, such as leafy greens, orange and red fruits and vegetables, and herbs and spices, can help improve overall health. However, it is important to note that factors such as food processing and cooking methods can affect carotenoid absorption. Thus, it is essential to consume a balanced and varied diet to ensure adequate intake of these beneficial pigments.