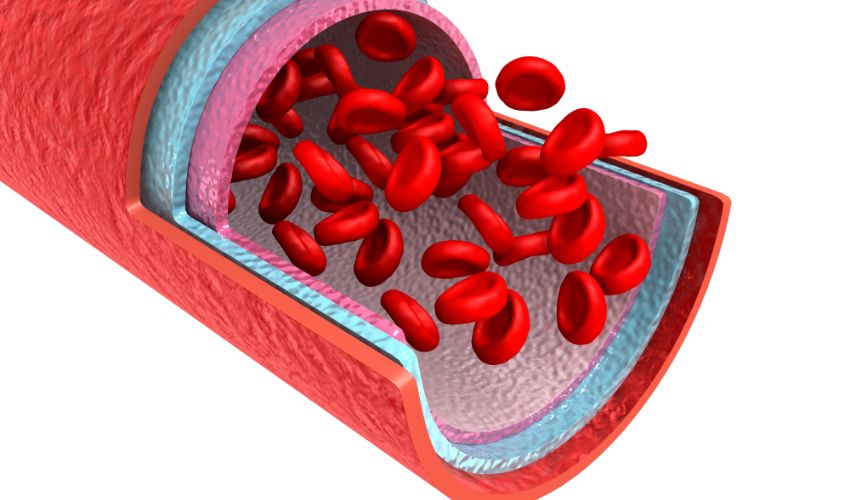
Red blood cells (RBCs), also known as erythrocytes, are one of the essential components of the human body’s circulatory system. They are responsible for carrying oxygen to various tissues and organs and removing carbon dioxide from the body. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of red blood cells, their functions, production, and potential disorders.
Functions of Red Blood Cells:
Red blood cells play a crucial role in the body’s oxygen transport system. The following are some of their essential functions:
- Oxygen transport: The primary function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and organs.
- Carbon dioxide removal: Red blood cells also help remove carbon dioxide from the body by transporting it to the lungs, where it is expelled during exhalation.
- Acid-base balance: Red blood cells help maintain the body’s acid-base balance by regulating the levels of hydrogen ions (H+) in the blood.
- Blood clotting: Red blood cells contain substances that help promote blood clotting, which is essential in preventing excessive bleeding.
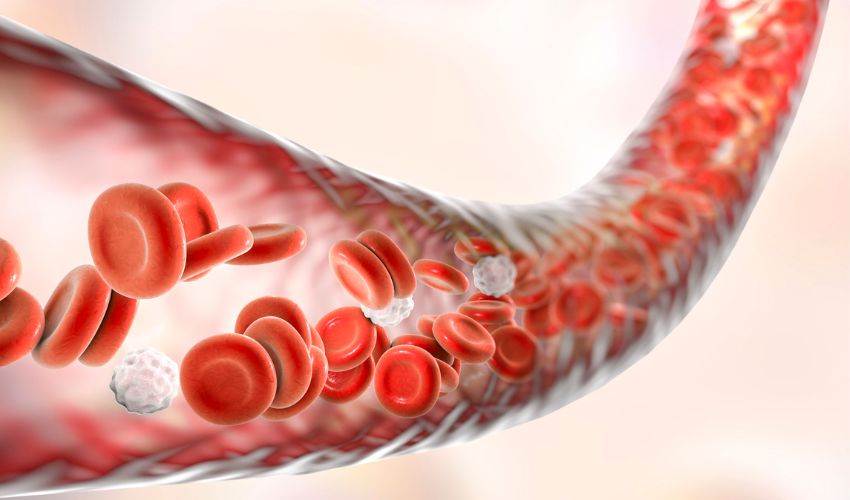
Production of Red Blood Cells:
The production of red blood cells occurs in the bone marrow. The following are some of the essential factors that influence the production of red blood cells:
- Hormones: The hormone erythropoietin, produced by the kidneys, stimulates the production of red blood cells.
- Nutrients: Adequate intake of nutrients such as iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid is crucial for the production of red blood cells.
- Oxygen levels: Low oxygen levels in the body, such as during high-altitude exposure, can stimulate the production of red blood cells.
Disorders of Red Blood Cells:
Several disorders can affect the production and function of red blood cells. The following are some of the most common:
- Anemia: Anemia occurs when there are not enough red blood cells in the body or when they are not functioning correctly. This can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and other symptoms.
- Sickle cell disease: Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects the shape of red blood cells, making them crescent-shaped instead of round. This can cause them to get stuck in small blood vessels, leading to pain and other complications.
- Polycythemia: Polycythemia is a condition in which there are too many red blood cells in the body, leading to thickening of the blood and an increased risk of blood clots.
FAQs:
What is the lifespan of a red blood cell?
The lifespan of a red blood cell is approximately 120 days.
Can red blood cells be produced outside the body?
Yes, red blood cells can be produced outside the body using stem cell technology.
What causes anemia?
Anemia can be caused by several factors, including iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, and blood loss.
Can blood transfusions help treat anemia?
Yes, blood transfusions can help treat anemia by increasing the number of red blood cells in the body.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Symptoms of sickle cell disease can include pain, fatigue, jaundice, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Conclusion:
Red blood cells are one of the essential components of the human body’s circulatory system. Their functions, production, and potential disorders are critical areas of study in the field of medicine. Understanding these aspects of red blood cells can help individuals take better care of their health and prevent potential health problems related to their red blood cells. Adequate nutrient intake, regular exercise, and regular blood tests can help ensure the proper functioning of red blood cells and maintain optimal health.
In conclusion, the importance of red blood cells cannot be overstated. These tiny cells play a vital role in maintaining the body’s oxygen supply, removing carbon dioxide, and ensuring proper blood clotting. Disorders related to red blood cells can lead to severe health problems, making it essential to understand their production and functions. By taking steps to promote the proper functioning of red blood cells, individuals can ensure their continued health and well-being.