Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body cannot produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness. Recognizing the early signs of diabetes is crucial to managing the condition and preventing complications. In this article, we will discuss the most common symptoms of diabetes and how to recognize them early on.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Increased Thirst and Urination
One of the most common symptoms of diabetes is increased thirst and urination. This occurs because the body is trying to flush out excess glucose in the blood through urine. As a result, you may feel the need to urinate more often, even waking up in the middle of the night to use the bathroom.
Hunger and Fatigue
Another symptom of diabetes is increased hunger and fatigue. This happens because the body is unable to convert glucose into energy, causing you to feel tired and hungry even after eating.
Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can also cause blurred vision, as excess glucose in the blood can damage the blood vessels in the eyes. This can lead to a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which can cause permanent damage to the eyes if left untreated.
Slow Healing
People with diabetes may also experience slow healing of wounds and cuts. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the body, leading to poor circulation and slower healing.
Numbness and Tingling
Another symptom of diabetes is numbness and tingling in the hands and feet. This is caused by nerve damage, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. If left untreated, diabetic neuropathy can cause permanent nerve damage and loss of sensation in the affected areas.

Lifestyle Changes to Manage Diabetes Symptoms
Managing diabetes symptoms requires making significant lifestyle changes, including:
- Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet: This means avoiding processed and sugary foods and increasing your intake of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Losing weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
- Exercising regularly: Physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of complications.
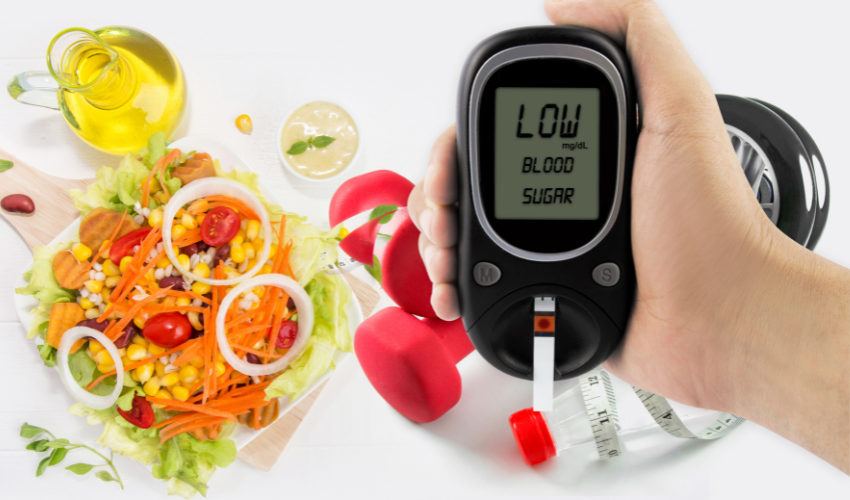
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Checking your blood sugar levels regularly can help you adjust your medication and lifestyle habits as needed.
- Taking medication as prescribed: Your doctor may prescribe medications such as insulin or oral medications to help regulate blood sugar levels.
By making these changes, you can effectively manage your diabetes symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
FAQs
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when the body attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or is unable to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.
Can diabetes be cured?
While there is currently no cure for diabetes, it can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Who is at risk for diabetes?
Anyone can develop diabetes, but certain factors can increase your risk. These include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Diabetes is typically diagnosed with a blood test that measures blood sugar levels. Your doctor may also order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of diabetes you have.
What are the complications of diabetes?
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and blindness.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of diabetes is crucial to managing the condition and preventing complications. If you experience any of the symptoms discussed in this article, it is important to talk to your doctor and get tested for diabetes. With proper treatment and lifestyle changes, diabetes can be managed effectively, allowing you to live a healthy and active life.






















