Clots, also known as thrombosis, occur when blood thickens and forms a solid mass within a blood vessel. Clots can be harmful or even life-threatening, depending on where they form and whether they travel to other parts of the body. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for clots can help you take proactive steps to protect your health.
Risk Factors:
There are several risk factors that can increase your likelihood of developing clots. Some of the most common risk factors include being overweight or obese, smoking, having a sedentary lifestyle, being over the age of 60, and having certain medical conditions such as cancer or heart disease. Women who are pregnant or taking hormonal birth control are also at increased risk for clots.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of clots can vary depending on where the clot forms in the body. In some cases, clots may not cause any symptoms at all. However, some common symptoms of clots can include swelling, warmth, redness, or pain in the affected area. If a clot travels to the lungs, it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away.
Diagnosis:
Clots are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exam, imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans, and blood tests. Your doctor may also ask about your medical history and any medications you are taking.
Treatment:
Treatment for clots may depend on the location and severity of the clot. Medications such as anticoagulants or thrombolytics may be prescribed to help dissolve the clot and prevent it from getting larger. Wearing compression stockings can also help to reduce swelling and improve circulation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot.
Prevention:
There are several preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing clots. Regular exercise can help to improve circulation and reduce the risk of clots. Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and taking preventive medications can also help to reduce your risk. If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of clots, your doctor may recommend additional preventive measures.
Bullet Points:
- Clots are a type of blood clot that can cause serious health problems.
- There are several types of clots, including DVT, PE, stroke, and heart attack.
- Risk factors for clots include age, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, medical conditions, and medications.
- Symptoms of clots can include leg pain and swelling, chest pain and shortness of breath, numbness or weakness on one side of the body, sudden severe headache, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Diagnosis of clots typically involves a physical exam, imaging tests, and blood tests.
- Treatment options for clots may include anticoagulants, thrombolytics, compression stockings, and surgery.
- Preventive measures for clots include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, taking preventive medications, and wearing compression stockings.
- Seek medical attention immediately if you experience symptoms of a clot, such as sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or difficulty speaking.
FAQs:
What causes clots?
Clots can be caused by various factors, including prolonged immobility, surgery, pregnancy, hormonal birth control, and certain medical conditions.
Who is at risk for clots?
Anyone can develop a clot, but certain factors can increase the risk, such as being overweight, having a family history of clots, smoking, being over the age of 60, and having certain medical conditions such as cancer or heart disease.
Can clots be prevented?
Yes, there are several preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing clots. These include exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, taking preventive medications, and wearing compression stockings.
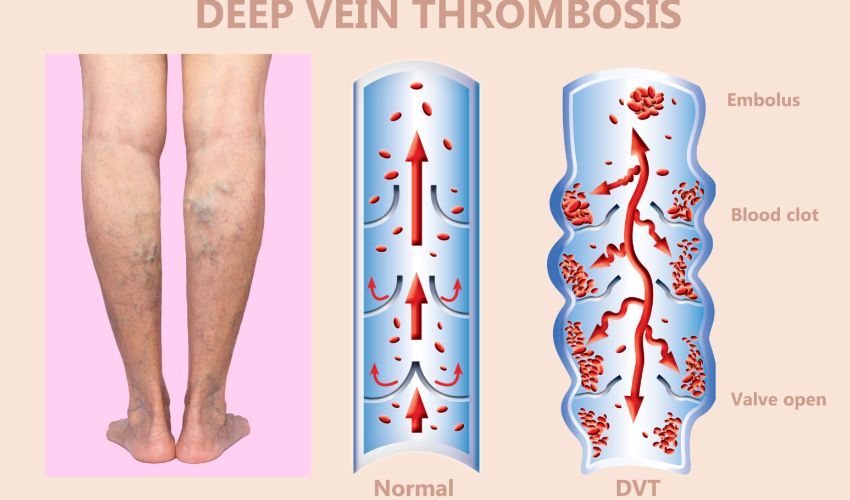
How are clots diagnosed?
Clots are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exam, imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans, and blood tests.
What are the treatment options for clots?
Treatment for clots may include medications such as anticoagulants or thrombolytics, wearing compression stockings, and in some cases, surgery.
Conclusion:
Clots can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, but with the right knowledge and preventive measures, they can be managed effectively. It’s important to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms of clots, and to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a clot. By taking steps to prevent clots, you can reduce your risk and improve your overall health and well-being.