Fertilizers are an essential element in gardening, farming, and agriculture. They provide plants with the necessary nutrients to grow healthy and strong, increasing their yield and quality. However, with so many types and brands of fertilizers available in the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your plants. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about fertilizers to help you make informed decisions and boost your plants’ growth.
Types of Fertilizers:
There are two main types of fertilizers: organic and inorganic. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as animal waste, compost, and plant residues. They release nutrients slowly and improve the soil structure, promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, are made from synthetic compounds, such as ammonium nitrate and potassium sulfate. They provide plants with nutrients in a concentrated form, but they can also harm the environment if not used properly.
Composition of Fertilizers:
Fertilizers contain three essential macronutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). Nitrogen is necessary for the formation of proteins and chlorophyll, promoting leaf growth and plant vigor. Phosphorus is vital for root development and fruit production, while potassium helps regulate water balance and increase disease resistance. In addition to NPK, fertilizers may also contain micronutrients, such as iron, zinc, and manganese, which are required in smaller amounts but are still essential for plant growth.
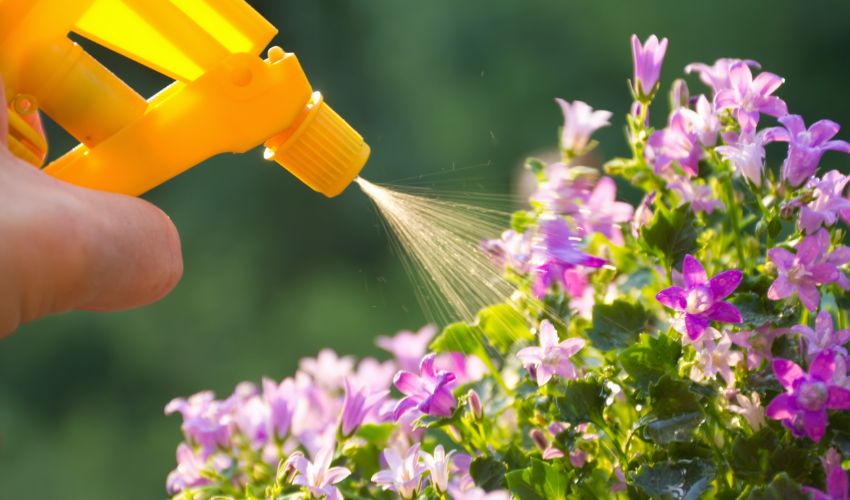

Application Methods:
Fertilizers can be applied in various ways, depending on the plant’s needs and the fertilizer type. Some common methods include:
- Broadcasting: Sprinkling fertilizers over a large area, such as a lawn, using a spreader or by hand.
- Foliar spraying: Applying a diluted fertilizer solution directly onto the leaves using a spray bottle or sprayer.
- Side-dressing: Placing fertilizer granules or liquid next to the plant’s roots or in the planting hole.
- Soil incorporation: Mixing fertilizers into the soil before planting or during cultivation.
Benefits of Fertilizers:
Using fertilizers can provide numerous benefits to plants and the environment, such as:
- Increased yield and quality of crops and flowers
- Improved soil fertility and structure
- Reduced soil erosion and water runoff
- Enhanced disease and pest resistance
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint
FAQs:
How often should I fertilize my plants?
The frequency of fertilization depends on the plant’s growth stage, soil fertility, and fertilizer type. Generally, it is recommended to fertilize once a month during the growing season and reduce the frequency during the dormant season.
Can I use too much fertilizer?
Yes, using too much fertilizer can harm plants by burning their roots or causing nutrient imbalances. It can also pollute waterways and contribute to eutrophication, a phenomenon that leads to algal blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic ecosystems.
What is the difference between slow-release and fast-release fertilizers?
Slow-release fertilizers release nutrients gradually over an extended period, providing a steady supply to plants. Fast-release fertilizers, on the other hand, release nutrients quickly, providing a rapid boost but also increasing the risk of over-fertilization.
Can I make my own organic fertilizer?
Yes, you can make organic fertilizer using household waste, such as kitchen scraps, leaves, and grass clippings. Composting is a simple and effective way to convert organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments. You can also make organic teas by steeping compost or other organic materials in water and using the resulting solution as a foliar spray or soil drench.

Are there any alternatives to chemical fertilizers?
Yes, there are many natural alternatives to chemical fertilizers, such as compost, manure, bone meal, fish emulsion, and seaweed extract. These products are often less expensive, more sustainable, and safer for the environment than synthetic fertilizers.
Conclusion:
Fertilizers play a crucial role in ensuring the health and productivity of plants. By understanding the types, composition, and application methods of fertilizers, you can make informed choices and help your plants thrive. Remember to choose the right fertilizer for your plants’ needs, follow the recommended application rates, and be mindful of the potential environmental impacts. With the right approach, fertilizers can help you achieve a lush and bountiful garden or farm.