Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions such as cell growth, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production. However, our body cannot produce folate, and we have to obtain it through our diet or supplements. Folate deficiency can lead to various health problems, including anemia, birth defects, and neurological disorders. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for folate deficiency symptoms.
Symptoms of Folate Deficiency:
Folate deficiency symptoms can vary from person to person, and they can be mild or severe. The following are the common symptoms of folate deficiency:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Mouth sores or ulcers
- Tongue swelling
- Diarrhea
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Depression
- Confusion
- Irritability
Causes of Folate Deficiency:
Folate deficiency can occur due to various reasons, such as:
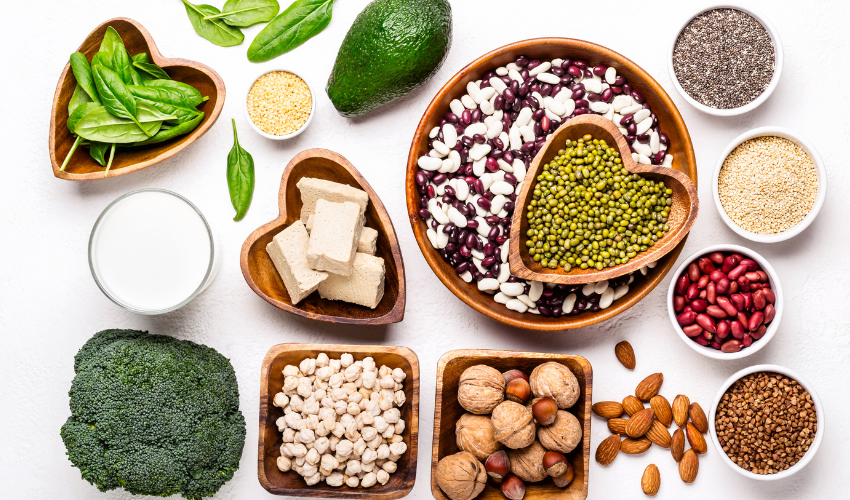
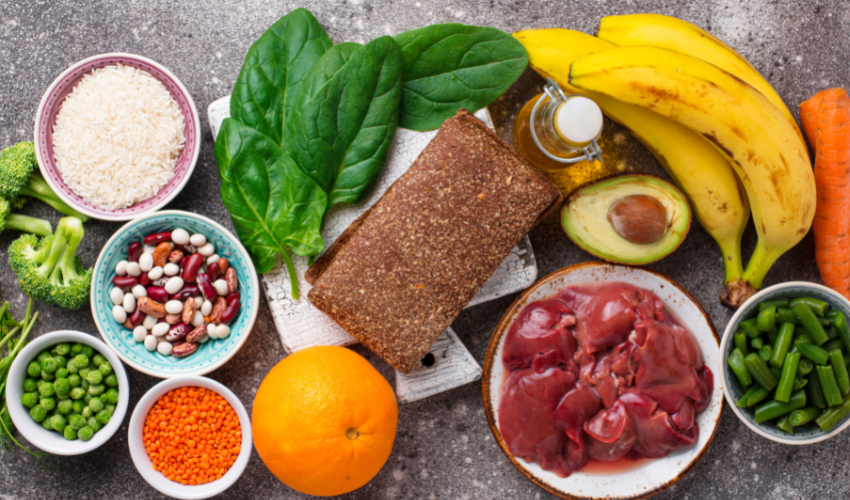
- Inadequate dietary intake: Folate-rich foods include leafy green vegetables, fruits, and legumes. People who follow a strict vegetarian or vegan diet may be at a higher risk of folate deficiency.
- Malabsorption: Certain medical conditions such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and chronic diarrhea can affect the body’s ability to absorb folate.
- Alcoholism: Alcohol interferes with folate absorption, and heavy drinkers may be at a higher risk of folate deficiency.
- Medications: Certain medications such as methotrexate, phenytoin, and sulfasalazine can interfere with folate absorption and increase the risk of folate deficiency.
Treatment Options for Folate Deficiency:
The treatment for folate deficiency depends on the severity of the deficiency and the underlying cause. The following are the common treatment options for folate deficiency:
- Dietary changes: Including folate-rich foods in the diet can help increase folate levels. Some of the foods rich in folate are spinach, asparagus, broccoli, lentils, and avocado.
- Supplements: Folate supplements are available in the form of tablets, capsules, and injections. The dosage and form of the supplement depend on the severity of the deficiency.
- Treating underlying conditions: If folate deficiency is due to an underlying medical condition, treating the condition can help improve folate levels.

FAQs:
How is folate deficiency diagnosed?
Folate deficiency can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of folate in the blood.
Is folate deficiency common?
Folate deficiency is not very common, but certain groups of people, such as pregnant women and people with certain medical conditions, are at a higher risk of folate deficiency.
What are the long-term effects of folate deficiency?
Long-term folate deficiency can lead to various health problems such as anemia, birth defects, and neurological disorders.
Can folate deficiency affect mental health?
Yes, folate deficiency can cause symptoms such as depression, confusion, and irritability.
Can folate deficiency be prevented?
Yes, folate deficiency can be prevented by including folate-rich foods in the diet or taking folate supplements.

Conclusion:
Folate deficiency is a common nutrient deficiency that can lead to various symptoms and health complications. Understanding the symptoms of folate deficiency, its impacts, and how to manage it can help you maintain a healthy body and mind. By incorporating folate-rich foods in your diet and taking supplements as recommended by your healthcare provider, you can prevent and manage folate deficiency and its symptoms. If you suspect you have folate deficiency symptoms, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.