Type 2 diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how the body metabolizes sugar (glucose), which is an essential source of energy for the body’s cells. The condition occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone that regulates the absorption and use of glucose in the body.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 34 million Americans have type 2 diabetes, and about 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes, a condition that can lead to type 2 diabetes if left untreated. This article provides an overview of type 2 diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes:
Type 2 diabetes can develop at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in middle-aged and older adults. The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is unknown, but several factors can increase the risk of developing the condition, including:
- Family history of diabetes
- Being overweight or obese
- Physical inactivity
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Symptoms:
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop gradually and may not be noticeable at first. Some of the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Hunger pangs
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or infections
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
Treatment:
The goal of treating type 2 diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels within the target range. Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight loss can help manage blood sugar levels effectively. Some of the treatment options available for type 2 diabetes include:
- Oral medications: Several types of oral medications can help lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. These medications work by increasing insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose absorption in the intestines, or stimulating insulin production in the pancreas.
- Insulin therapy: Some people with type 2 diabetes may need insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin therapy involves injecting insulin into the body to help glucose enter the body’s cells.
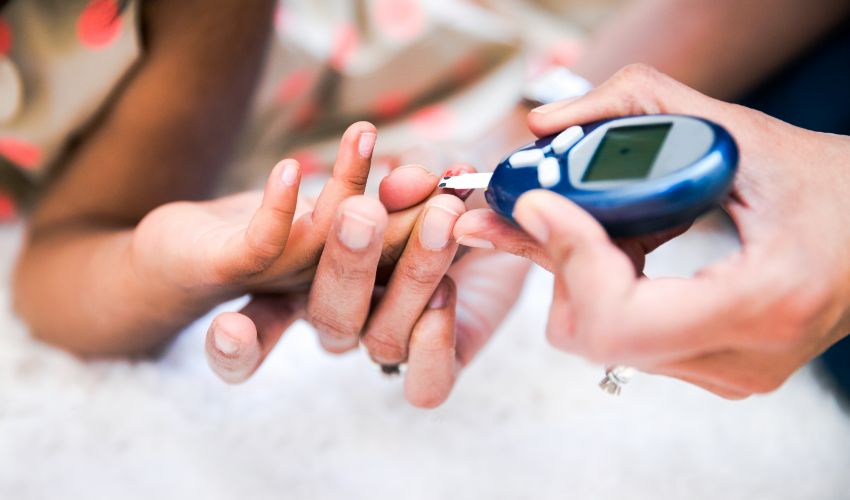
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. People with type 2 diabetes can monitor their blood sugar levels at home using a blood glucose meter.
Prevention:
Making healthy lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some of the ways to prevent type 2 diabetes include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Managing stress effectively
- Getting regular check-ups to monitor blood sugar levels and detect any health problems early on.
Bullet Points:
- Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and insulin resistance.
- Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
- Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes involves blood sugar testing, and treatment options include medications, insulin therapy, and surgery.
- Lifestyle changes such as healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, weight loss, and stress management are essential for managing type 2 diabetes.
- Medications for managing type 2 diabetes include oral medications, injectables, and insulin therapy.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels using blood sugar monitoring devices and HbA1c tests is essential for managing type 2 diabetes.
FAQs:
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors and is characterized by insulin resistance.
Can type 2 diabetes be cured?
Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications.

How often should I get my blood sugar checked if I have type 2 diabetes?
The frequency of blood sugar testing depends on various factors such as the severity of diabetes and the treatment plan. Your doctor can advise you on how often you should get your blood sugar checked.
Can type 2 diabetes lead to other health complications?
Yes, if left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes can lead to other health complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and blindness.
Is it possible to prevent type 2 diabetes?
Yes, making healthy lifestyle choices such as maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, and eating a balanced diet can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion:
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic medical condition that requires long-term management. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for managing this condition can help individuals living with type 2 diabetes lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Lifestyle changes such as healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, weight loss, and stress management are essential for managing type 2 diabetes. Medications and insulin therapy can also be used to manage blood sugar levels effectively. It is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and seek medical attention if necessary to avoid serious health complications associated with type 2 diabetes.