Caused of Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a debilitating illness that can rob people of their memories, their independence, and their quality of life. Despite decades of research, the exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are not yet fully understood. In this article, we will explore the various factors that are believed to contribute to the development and progression of this disease.
Genetics and Alzheimer’s Disease
1. Family History and Alzheimer’s Disease
2. Gene Mutations and Alzheimer’s Disease
Research has shown that genetics plays a significant role in the development caused of Alzheimer’s disease. Individuals who have a family history of Alzheimer’s disease are at a higher risk of developing the illness. There are also specific gene mutations that have been identified as being associated with an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Age and Alzheimer’s Disease
1. Age-related Changes in the Brain
2. Impact of Aging on Brain Function
As people age, the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease increases. The aging process is associated with changes in the brain, including a reduction in brain volume, a decrease in blood flow to the brain, and an increase in inflammation. These changes can lead to a decline in cognitive function, which is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.

Lifestyle Factors and Alzheimer’s Disease
1. Diet and Alzheimer’s Disease
2. Exercise and Alzheimer’s Disease
3. Sleep and Alzheimer’s Disease
Certain lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. For example, a diet high in saturated fats and processed foods has been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline. On the other hand, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.

Brain Changes and Alzheimer’s Disease
1. Brain Plaques and Alzheimer’s Disease
2. Neurofibrillary Tangles and Alzheimer’s Disease
3. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease
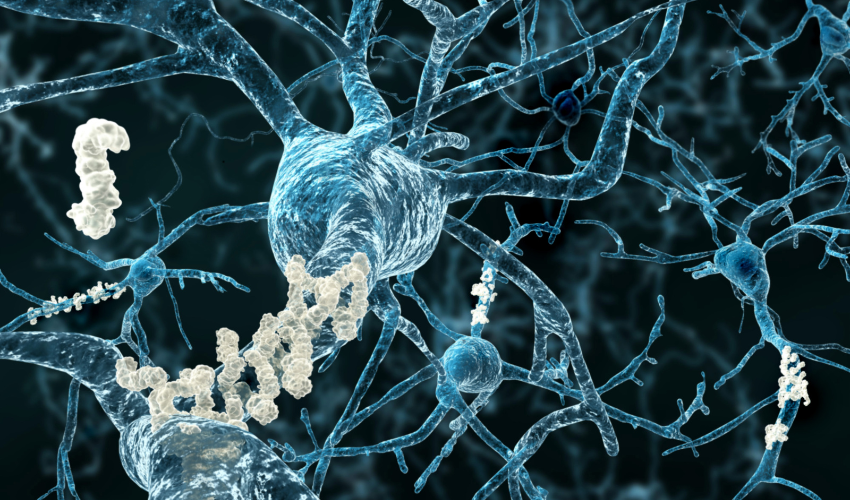
The brain changes that occur in Alzheimer’s disease include the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These changes can lead to inflammation in the brain, which can cause damage to brain cells and interfere with cognitive function.

FAQs:
Can Alzheimer’s disease be inherited?
Yes, individuals who have a family history of Alzheimer’s disease are at an increased risk of developing the illness.
Can lifestyle factors impact the development of Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, certain lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and sleep can impact the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
What are beta-amyloid plaques?
Beta-amyloid plaques are clumps of protein that accumulate in the brain of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
What are neurofibrillary tangles?
Neurofibrillary tangles are abnormal accumulations of a protein called tau that occur inside nerve cells.
Is there a cure for Alzheimer’s disease?
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. However, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms of the illness.
Conclusion:
Caused of Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating illness that can have a significant impact on individuals and their families. While the exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are not yet fully understood, research has identified several factors that contribute to the development and progression of the illness.
Genetics, age, lifestyle factors, and brain changes are all believed to play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. However, there is no single cause of the illness, and it is likely that a combination of factors contributes to its development.
Understanding the causes of Alzheimer’s disease is essential for the development of effective treatments and interventions that can help individuals manage the symptoms of the illness and maintain their independence and quality of life. While there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, ongoing research and advancements in medical technology offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those living with the illness.