Mass production refers to the process of producing large quantities of standardized products, usually through assembly line techniques. This method of production is characterized by efficiency, consistency, and lower costs, making it a popular choice for many industries. In this article, we will explore the basics of mass production and its impact on the manufacturing industry.
The History of Mass Production
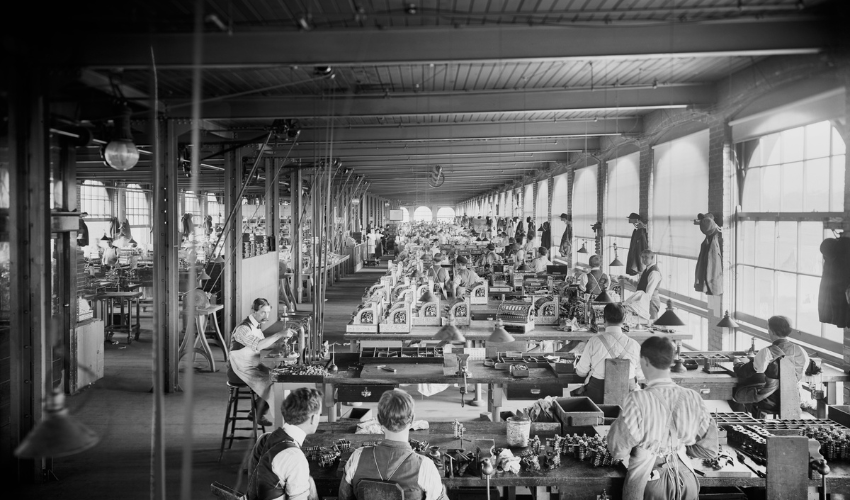

Mass production has its roots in the industrial revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. It was during this time that new technologies, such as the steam engine and the power loom, were developed, allowing for increased efficiency in the production of goods. However, it was not until the development of the assembly line by Henry Ford in the early 20th century that mass production truly took off.
Principles of Mass Production
It is based on three key elements: standardization, specialization, and efficiency.
- Standardization
It relies on the use of standardized parts, tools, and machinery. This ensures that products are consistent in quality and design, and it makes it easier to produce large quantities of products quickly and efficiently.
- Specialization
It also relies on the use of specialized machinery and workers. Each worker is responsible for a specific task, and the tasks are organized in an assembly line. This ensures that each worker is highly skilled at their specific task, and it enables products to be produced quickly and efficiently.
- Efficiency
It is designed to be as efficient as possible. This means that products are produced quickly, with minimal waste and maximum efficiency. The use of specialized machinery and workers, along with standardized parts and processes. This makes it one of the most efficient manufacturing methods available.
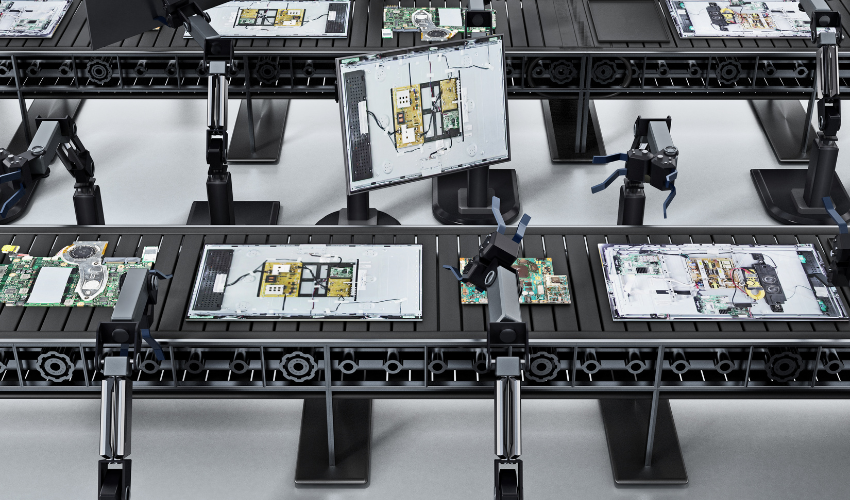

The Advantages of Mass Production
The primary advantage of mass production is cost-effectiveness. By producing large quantities of standardized products, manufacturers can spread their fixed costs, such as equipment and labor, over a larger number of products. This results in lower costs per unit, making mass-produced goods more affordable for consumers.
In addition to cost savings, it also offers other benefits, such as consistency and efficiency. By using standardized processes and machines, manufacturers can ensure that each product is of high quality and meets the same specifications. This consistency leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Mass production also allows for faster production times, as assembly line techniques allow for products to be produced quickly and efficiently. This is particularly useful in industries where there is a high demand for goods. It allows manufacturers to keep up with demand and avoid stock shortages.
The Disadvantages of Mass Production
Despite its many benefits, mass production is not without its drawbacks. One of the biggest disadvantages is the loss of creativity and uniqueness in the production process. As products are standardized and produced en masse, there is less room for individuality and creativity in the design and manufacturing process.
Another disadvantage is that it can result in job loss, as machines and automation replace human labor. This can lead to a decrease in the number of jobs available in certain industries and can negatively impact local economies.
Finally, mass production can also result in environmental degradation, as manufacturers often use large quantities of resources, such as energy and raw materials, to produce goods. This can lead to increased pollution and a negative impact on the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between mass production and mass customization?
Mass production refers to the process of producing large quantities of standardized products, while mass customization refers to the process of producing customized products in large quantities. Mass customization allows manufacturers to offer customers unique products while still maintaining the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of mass production.
What industries use mass production?
It is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. It is particularly common in industries where there is a high demand for goods and where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are important factors.
What are the environmental impacts of mass production?
It can have a negative impact on the environment. It often involves the use of large quantities of resources, such as energy and raw materials. This can lead to increased pollution and a negative impact on the environment.
What are the benefits for consumers?
For consumers, the primary benefit is the lower cost of goods. By producing large quantities of standardized products, manufacturers can spread their costs over a larger number of products, resulting in lower costs per unit. This makes mass-produced goods more affordable for consumers. In addition, it can also result in increased consistency and reliability, as manufacturers use standardized processes to ensure that each product meets the same high-quality standards.
What are the disadvantages for workers?
One of the biggest disadvantages for workers is the loss of jobs due to automation and the use of machines. As assembly line techniques replace human labor, workers may find it more difficult to find employment in certain industries. Additionally, mass production can also result in monotonous and repetitive work. This leads to low job satisfaction for workers on the assembly line.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mass production is a popular and effective method of production, characterized by its efficiency, consistency, and cost-effectiveness. It has revolutionized the manufacturing industry and has made it possible for manufacturers to produce large quantities of standardized products quickly and efficiently. However, it is important to consider its potential drawbacks, such as the loss of creativity, job loss, and environmental degradation, in order to make informed decisions about its use in the future. Ultimately, the goal should be to strike a balance between the benefits of mass production and its potential drawbacks. That is in order to ensure sustainable and responsible production processes.