Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are the building blocks of the nervous system. They are responsible for transmitting and receiving signals that allow us to perceive and interact with the world around us. These specialized cells are capable of communicating with each other and coordinating complex functions, making them essential to our survival. In this article, we will explore the wonders of nerve cells, their structure, function, and the role they play in our daily lives.
What are Nerve Cells?
Nerve cells, or neurons, are specialized cells that are responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. They are the building blocks of the nervous system and are found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system.
Structure of Nerve Cells
Nerve cells have a unique structure that allows them to transmit and receive signals. They consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles necessary for the cell’s survival. Dendrites are short, branching extensions that receive signals from other neurons. The axon is a long, slender extension that transmits signals to other neurons.
Types of Nerve Cells
There are three main types of nerve cells: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting information from sensory organs, such as the eyes and ears, to the brain. Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain to muscles and glands. Interneurons are responsible for communicating between sensory and motor neurons and are found in the brain and spinal cord.
How Nerve Cells Work
Nerve cells communicate with each other through a process called synaptic transmission. When an electrical signal, or action potential, reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the dendrites of other neurons, triggering an electrical signal in that neuron.
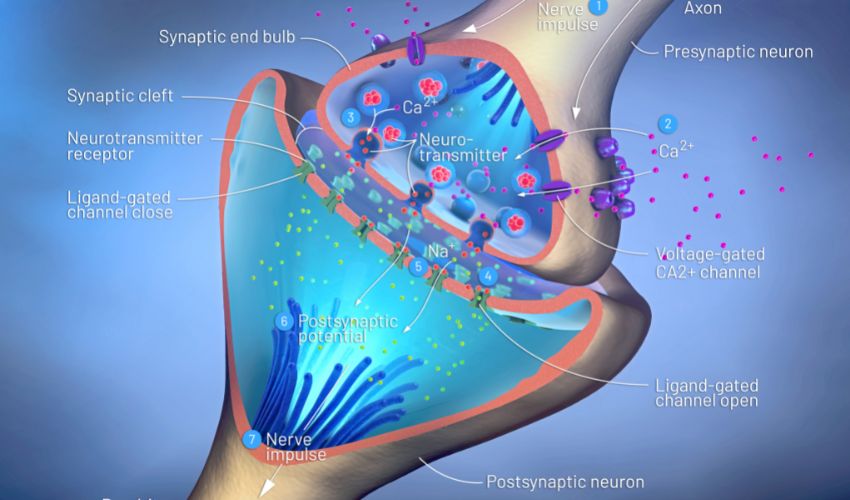
The Role of Nerve Cells in the Nervous System
Nerve cells are essential to the functioning of the nervous system. They allow us to perceive and interact with the world around us, control our movements, and regulate our bodily functions. They are also responsible for the processing of information and the creation of memories.
Diseases and Disorders of Nerve Cells
There are many diseases and disorders that can affect nerve cells. These include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). These diseases can cause a variety of symptoms, including memory loss, tremors, and muscle weakness.
FAQs:
Can nerve cells regenerate?
In general, nerve cells cannot regenerate. However, some studies have suggested that certain types of nerve cells may be capable of regenerating under certain conditions.
What happens when nerve cells die?
When nerve cells die, they are not replaced. This can result in a loss of function in the affected area.
Can nerve cells communicate with other types of cells?
Nerve cells can communicate with other types of cells through chemical signaling. For example, neurotransmitters released by nerve cells can affect the activity of muscle cells and gland cells.
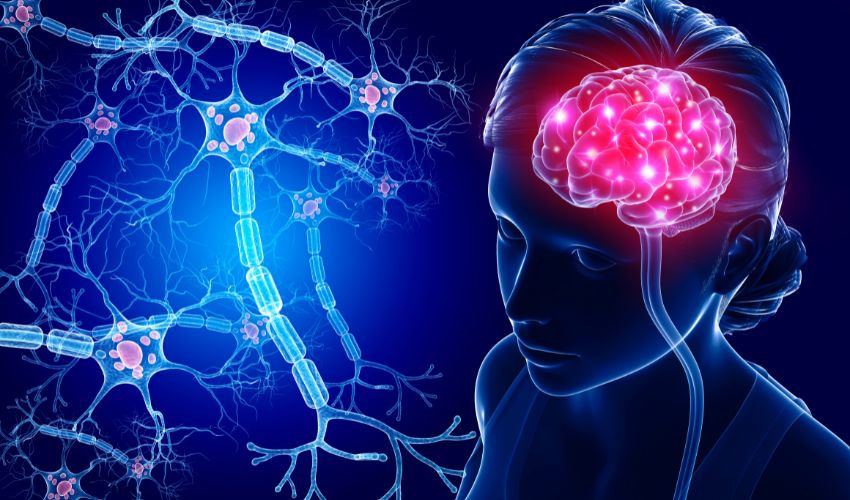
How many nerve cells are in the brain?
There are approximately 100 billion nerve cells in the human brain, making it one of the most complex structures in the known universe.
Can nerve cells change their shape?
Yes, nerve cells can change their shape in response to changes in the environment. This is known as plasticity and is an essential component of learning and memory.
Conclusion:
Nerve cells, or neurons, are an essential component of the nervous system. They allow us to perceive and interact with the world around us, control our movements, and regulate our bodily functions. Understanding the structure and function of nerve cells can help us appreciate the incredible complexity of the human body and the wonders of the natural world. Although many diseases and disorders can affect nerve cells, ongoing research is exploring new ways to protect and regenerate these critical cells. By continuing to study nerve cells, we can unlock new insights into the workings of the brain and the human body.